This article has been reviewed by:
Martina Schaale
Dental hygienist
More than half of the population aged 35 and over suffer from periodontitis. In people aged 65 and over, the number of those affected rises to almost two thirds and from the age of 75, around 9 out of 10 people have periodontitis. These are the results of the German Oral Health Study V from 2016, making periodontitis one of the most common diseases and one more reason not to skip your regular appointments with the dentist!
Periodontitis or Parodontitis - What is it?
But what exactly is periodontitis? Periodontitis, also known colloquially as periodontitis, is a serious, inflammatory disease of the dental apparatus. Depending on its severity, periodontitis not only affects the gums, but can also spread to the root of the tooth and even the bone.
The periodontium is made up of the following structures that can be affected:
- The gums
- The tooth root
- The tooth-bearing bone
- The tissue that holds the tooth in the bone.
Together with the ending “-itis”, which in medicine describes an inflammatory process, this results in periodontitis. In short: periodontitis = inflammation of the periodontium.

IMPORTANT: If periodontitis and its pockets remain untreated, there is a risk of tooth loss. It also increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, premature births and dementia.
Causes and development of periodontitis
Die Ursache einer Parodontitis sind immer Bakterien. Zwar gehören Bakterien zu unserem oralen Mikrobiom – sowohl „gute“ als auch „schlechte“ leben in einem ökologischen Gleichgewicht. Allerdings kann dieses Gleichgewicht durch bestimmte Risikofaktoren kippen. Wenn das passiert, können sich die krankmachenden Keime und der bakterielle Biofilm rasant vermehren und es kommt zu Zahnfleischrückgang.
The risk factors for periodontitis
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of periodontitis. On the one hand, nutrition plays a role, as deficiencies can affect the immune system and the body’s ability to fight inflammation. Obesity and diabetes are also risk factors for periodontitis. Habits such as smoking or breathing through the mouth also affect the balance of our oral flora, favouring the development of periodontitis. Fillings and crowns can also pose a risk, for example if they are poorly adapted to the gums, defective or even if there is an intolerance to the material, which can irritate the gums.


INFO: Gum recession caused by stress should not be underestimated. Physical and mental stress ensure that inflammatory substances are released.
Is periodontitis hereditary?
Genetic predisposition does indeed play a role in susceptibility to periodontitis and the severity of its progression. This is due to a gene complex that is hereditary and is responsible for the production of anti-inflammatory substances in the immune system. This gene complex is altered in around a third of the population, resulting in an overproduction of these immune defence substances. This has negative effects, as the inflammatory reactions are not inhibited but actually intensified and the patient’s own gums can also be attacked.
People who inherit this genetic change therefore have a greater risk of developing periodontitis.
Development and symptoms of periodontitis
Before periodontitis develops, gum inflammation first occurs, which is known as gingivitis in dentistry. Gingivitis is a mild periodontitis and is therefore still completely curable.

Gingivitis - The initial stage of periodontal diseas
With good dental care, a balanced diet and regular dental cleanings at your dentist, gingivitis does not lead to tissue and bone loss and mild periodontitis can be treated well. Nevertheless, gingivitis is the initial stage of periodontitis and should therefore be taken seriously. Even if the symptoms are not yet very pronounced, immediate action should be taken to prevent a more serious development.
What are the symptoms of mild periodontitis?
Gingivitis, a mild form of periodontitis, is not painful at first. The first sign is inflamed gums, which often manifest themselves with bleeding during or after brushing. Many people also notice receding gums, bad breath or slight mobility of the teeth.
The following symptoms are common with mild periodontitis:
- Gum bleeding
If your gums regularly bleed when you brush your teeth or even when you eat solid food, this could be an early sign of periodontitis. - Gum recession
Gingivitis causes the gums to recede, making the teeth appear longer. This is a sign that the gum tissue is receding and mild periodontitis is already present. - Sensitive teeth
Sensitivity to hot, cold or sweet foods and drinks can occur because the gums recede and expose parts of the tooth that are more sensitive. - Bad breath
Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth that doesn’t go away can be caused by a bacterial imbalance associated with periodontitis. - Pain when chewing
Pain or discomfort when chewing can indicate inflammation and damage to the tissue that supports the teeth and can therefore be one of the first signs of an inflammatory reaction. - Tooth loosening
If the teeth start to loosen, this may be due to progressive bone loss. However, this is more typical of later stages of periodontitis.
Is periodontitis contagious?
Here you can clearly say: Yes!
Periodontitis is contagious, as the bacteria can be transmitted via saliva. Your partner and children should therefore also visit the dentist so that a periodontal screening index can be carried out.
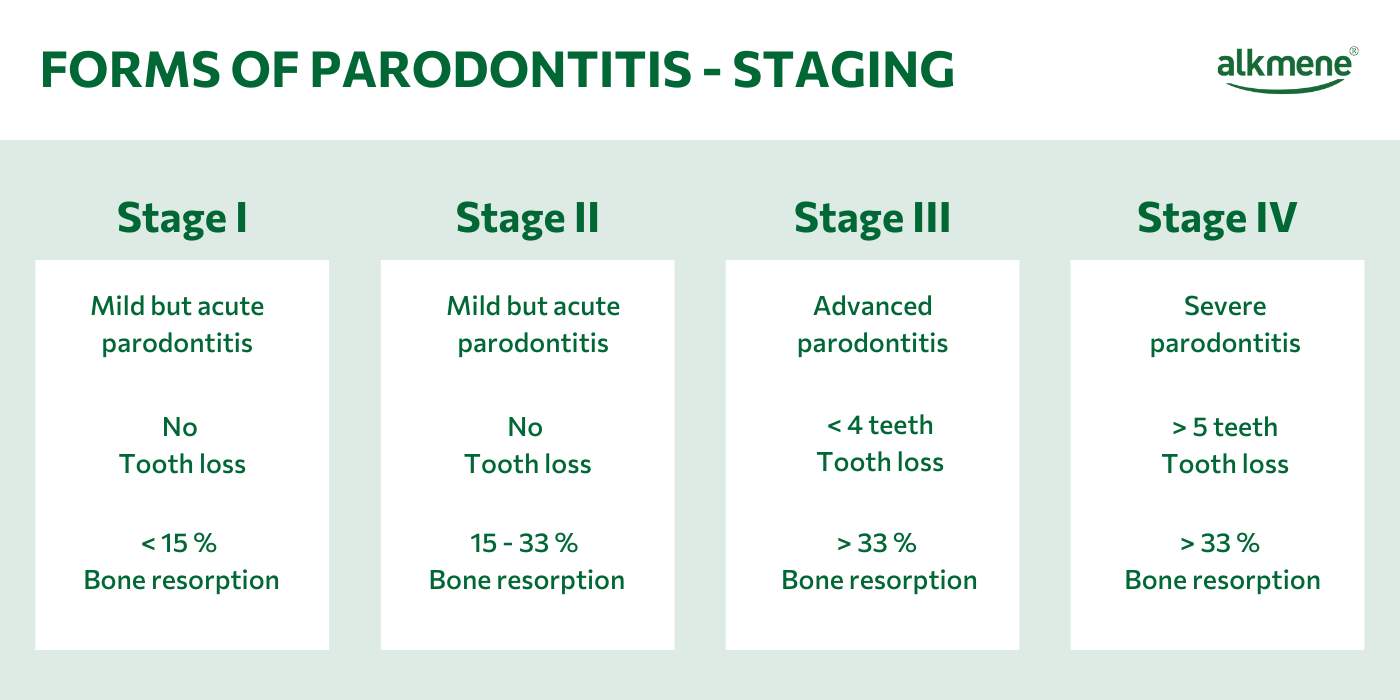
Forms and stages of periodontitis
Periodontitis is always a chronic disease. However, there are different forms and degrees of severity. Stages I and II describe mild but acute periodontitis. Stage III, on the other hand, is advanced periodontitis and stage IV is severe periodontitis. In the last two stages, tooth loss, tooth migration or tooth loosening may have already occurred.
The aggressive form of periodontitis, which usually affects younger people under the age of 35, leads to rapid bone and tissue loss. The formation of pus or secretions may also be possible.
Our product recommendations for parodontitis prophylaxis:
Periodontal treatment and the time afterwards - What do I need to consider
Are you about to have periodontal treatment or have you already had one? Then there are a few things you need to bear in mind.
How does periodontal treatment work
Diagnosis
First of all, your dentist will thoroughly examine your oral cavity and your teeth, for example to measure the pocket depth and diagnose periodontitis and its stage based on various factors. The examination may also include X-rays or a bacterial test, for example.
Treatment (basic therapy)
During periodontal treatment, your gum pockets are treated. This cleaning is not usually painful, as the gum pockets are anaesthetised in the vast majority of cases. The pockets are cleaned with ultrasound and special instruments and the bacterial biofilm is removed. The treatment can take several sessions.
Control
After a few weeks, the success of the treatment is checked during a follow-up check and further measures are initiated if necessary.
Further treatment
In severe cases or advanced periodontitis, further treatment methods such as surgical procedures or bone augmentation methods may also be required. You should discuss the procedure with your dentist, who will guide you through the treatment.
What are the costs of periodontal treatment?
The cost of treatment varies greatly depending on the extent and severity of the periodontitis. While the cost of the initial examination can be between €50 and €150, the cost of treatment can run into four figures. Surgical interventions are significantly more expensive than postponing antibiotics.
Basic periodontitis treatment is covered by statutory health insurance if certain criteria are met. These criteria include, for example, the diagnosis of periodontitis and a treatment plan. If further treatment or special procedures such as bone augmentation methods are required, these are often not covered by health insurance.

INFO: Implants or teeth that are already very mobile with severe bone loss are also not covered. Nevertheless, the treatment of periodontitis is very important in these cases because the bacteria in the oral cavity can otherwise migrate and recolonise cleaned root surfaces.
What needs to be considered after the treatment?
After the gum treatment, you should change your toothbrush and interdental brushes. You should continue to care for and brush your teeth as normal. In addition, an antibacterial mouthwash can help to maintain the bacterial balance in your mouth and reduce exposure to “bad” bacteria.

IMPORTANT: Periodontitis cannot be cured. It is a chronic disease, but you can live with it wonderfully if you keep your regular appointments for supportive periodontitis therapy (tooth cleaning after periodontitis treatment). Also try to reduce your risk factors, then you should not normally expect any further gum recession.
Can you treat periodontitis yourself?
No. Periodontitis is a serious bacterial disease. Without professional treatment, it can have serious consequences, some of which can cause irreversible damage. So if you suspect that you might be affected by periodontitis, you should always visit your dentist. This also applies if symptoms of mild periodontitis first become noticeable – the sooner action is taken, the better!